 |
| Tilia leaf |
- This is the second lesson; the first lesson about leaf vocabulary and identification is here.
Require for Observation: Sample clip art drawings for teachers to share with students below. Teachers should also have a few real leafs to show the class the: veins, stalk, stem and tips.
Method of Student Observation:
- A suitable leaf should be tom in order to show the tough and fibrous character of the veins, and the softer nature of the intermediate parts of the leaf. The arrangement of the veins should next be studied, holding the leaf up to the light and looking through it, when necessary, to render the smaller veins visible. Finally, the leaves should be classified according to their venation.
- As much as possible of this information should be obtained from the class.
- A plant may often be killed by cutting off all its leaves. Why is this?
How to Grade Study Notes For Student Journals: Every student will need a journal to write in weekly for this online nature study series. Teacher will assign the weekly content in advance.
- Make sure the facts are: written in complete sentences, the first word of each sentence capitalized, and a period should be included at the end of each sentence.
- Spell check your vocabulary and write the words correctly.
- Dress up your journal entries with student clip art, drawings of your own in color or in black and white.
- Student may also include photographs of their own taking for extra credit.
Look for the following facts about leaf anatomy inside of student journals. Assign a point value to the quality of the content.
- The veins (like the stalk and the midrib) contain fibers, and are, therefore, tough; while the other portions of the leaf are soft and cellular. The fibres are the vessels by which the sap circulates. The veins generally form a network, but sometimes they are parallel.
- Uses of Leaves for The Plant - Leaves are the breathing organs of the plant. They take in gaseous plantfood from the atmosphere. Leaves have microscopic holes ( stomata ) to enable them to perform these functions.)
- In the leaves, the sap of the plant is exposed to light and air. This causes the formation of starch, sugar, gum, and other substances required by the plant.
- To humans many leaves are used as food (cabbage, lettuce, cress), some for making beverages (tea), and many for the preparation of drugs.
Video at Youtube for Students to Watch:
- Structure of the leaf by FuseSchool
- Venation of leaf by 7activestudio
- Travel Deep Inside a Leaf by California Academy of Sciences
Draw the anatomy of a leaf and label it's parts. There is clip art below given as the teachers diagram examples. Students should either bring a leaf from home to draw and label it's parts or gather a leaf from the school playground on a walk with his or her classmates to do the same with. After drawing their own example of the leaf they may color it in with pencils or crayons.
Review What should be illustrate by the students:
- The stalk joins the leaf to the stem of the plant.
- The little branch-looking lines on the leaf are called veins.
- The stalk joins the leaf to the stem of the plant and runs up the middle of the leaf to the tip.
- There are two kinds of leaves called simple and compound. Identify the type you will draw.
Free Student Clip Art: Clip art may be printed from a home computer, a classroom computer or from a computer at a library and/or a local printing service provider. This may be done from multiple locations as needed because our education blog is online and available to the general public.
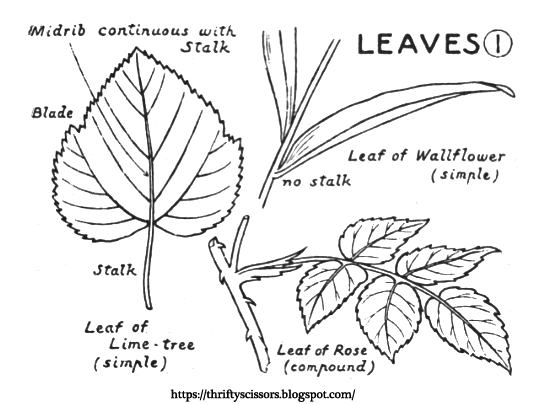 |
| Illustration of midrib, stalk, blade for the Lime tree. Illustration of Leaf of Wallflower and Leaf of Rose. |
 |
| Illustrated lily leaf with veins running side by side. Illustrated lime leaf with a network of veins. Illustrated small piece of leaf much enlarged showing cells and breathing holes. |

No comments:
Post a Comment
Folks, thanks for comments. These are all checked out before publishing. I can not publish spam, doing this negatively reflects upon 'how' my blog ranks and it also will make you look suspicious to those who own this software.
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.